고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문

1. OneToOne
OneToOneField를 사용했을 때
class BodyProfile(models.Model):
height_cm = models.DecimalField(max_digits=5, decimal_places=2)
weight_kg = models.DecimalField(max_digits=5, decimal_places=2)
feet_mm = models.DecimalField(max_digits=5, decimal_places=2)
class Meta:
db_table = 'body_profiles'
class User(models.Model):
email = models.EmailField(max_length=100)
password = models.CharField(max_length=500)
# 👇관계 정의
body_profile = models.OneToOneField(BodyProfile, on_delete=models.CASCADE, null=True, blank=True)
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
updated_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now=True)
class Meta:
db_table = 'users'

OneToOneField의 특징 - 참조하는 키값은 Unique 해야된다
OneToOneField를 사용하면 참조하는 foreign key에 Unique Key 옵션이 추가됩니다.
그래서 만약 한 명의 user가 참조하고 있는 body_profile 데이터를
다른 user가 참조하려 하면 에러가 납니다.
python manage.py shell 을 통해 테스트 해봅시다.
# body_profile에 data 입력
body_info = BodyProfile(height_cm=165, weight_kg=56, feet_mm=250)
body_info.save()
# user 두 명 생성 & 입력
person1 = User(email='moonionn@gmail.com', password='sOmE@Com^plicated_Pw')
person2 = User(email='django_man@django.co', password='SoMe$haSHeD19Pw')
person1.save()
person2.save()person1.body_profile = body_info
person1.save()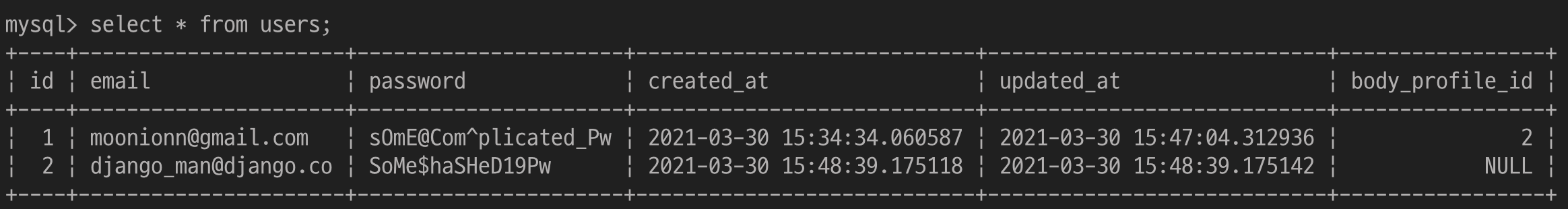
만약 여기서 django_man@django.co 에 똑같은 body_profile을 참조하려 하면
아래와 같은 에러가 발생합니다. (unique 값인데 duplicate entry 입력했다는 뜻)
django.db.utils.IntegrityError: (1062, "Duplicate entry '2' for key 'users_body_profile_id_bb2dba97_uniq'")
OneToOneField의 특징 - OneToOneField로 연결된 테이블은 서로를 정참조한다.
OneToOneField를 어느 테이블에서 지정해주었든간에 연결된 테이블은 서로를 정참조 하게 됩니다.
>>> person1.body_profile.feet_mm
Decimal('250.00')>>> body_info.user.email
'moonionn@gmail.com'
2. OneToMany
한 명의 유저는 여러 주소정보를 저장할 수 있습니다.
이 때 table의 관계는 OneToMany로 설정할 수 있습니다.
OneToMany 관계를 만들기 위해서는 ForeignKey를 지정해주어야 합니다.
# addresses 테이블 생성
class Address(models.Model):
# 👇관계 정의
user = models.ForeignKey(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
district = models.CharField(max_length=100)
address1 = models.CharField(max_length=200)
address2 = models.CharField(max_length=200)
postal_code = models.CharField(max_length=10)
class Meta:
db_table = 'addresses'
테이블을 생성했으면 python manage.py shell에서 객체를 생성하고 저장해봅시다.
>>> person1 = User.objects.get(pk=1)
>>> person1_addr = Address(
user=person1,
district='서울특별시',
address1='강남구 삼성2동',
address2='위워크 1층',
postal_code='000111'
)
>>> person1_addr.save()
ForeignKey 설정을 Address Class에서 했기 때문에
address 입장에서는 user를 바로 불러올 수 있습니다.
>>> addr1.user.email
'moonionn@gmail.com'
연결을 통해 더 멀리 있는 테이블로도 접근이 가능합니다.
>>> addr1.user.body_profile.weight_kg
Decimal('56.00')
하지만 user 입장에서 address 정보를 받기 위해서는 set을 사용해야 합니다.
# 그냥 address를 찍으면 에러 발생
>>> person1.address
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<console>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'User' object has no attribute 'address'# address_set을 이용하면 QuerySet을 불러올 수 있다.
>>> person1.address_set.values()
<QuerySet [{'id': 1, 'user_id': 1, 'district': '서울특별시', 'address1': '강남구 삼성2동', 'address2': '위워크 1층', 'postal_code': '000111'}]>
3. ManyToMany
한 명의 유저는 여러 쿠폰을 보유할 수 있고, 하나의 쿠폰은 여러 유저가 가질 수 있습니다.
따라서 이 관계는 다대다이며, 장고에서는 이 관계를 ManyToManyField로 표현할 수 있습니다.
class Coupon(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=100),
discount_price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2, null=True, blank=True)
discount_percent = models.DecimalField(max_digits=5, decimal_places=2, null=True, blank=True),
#👇관계 정의
owner = models.ManyToManyField(User, through='CouponUsers')
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
class Meta:
db_table = 'coupons'# 중간 테이블
class CouponUsers(models.Model):
user = models.ForeignKey(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
coupon = models.ForeignKey(Coupon, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True) #발급일
class Meta:
db_table = 'coupon_users'

다시 shell로 들어가서
작업해봅시다.
우선 쿠폰을 하나 만들어 줍니다.
>>> person1 = User.objects.get(pk=1)
>>> welcome_coupon = Coupon(name='가입환영 쿠폰', discount_percent=20)
>>> welcome_coupon.save()
다음, 관계 설정을 해줍니다.
ManyToMany 관계 설정이 Coupon class에서 이루어졌기 때문에
OneToMany와 마찬가지로 coupon에서만 바로 user를 불러올 수 있습니다.
user에서 coupon을 불러오려면 coupon_set을 이용해야 합니다.
이때 중간테이블에서 user를 참조하는 이름은 owner이기 때문에
owner라는 이름을 사용해 user를 불러올 수 있습니다.
>>> welcome_coupon.owner.add(person1)
반대로 user를 잡고 쿠폰을 발급해보겠습니다.
>>> person2 = User.objects.get(pk=2)
>>> person2.coupon_set.add(welcome_coupon)
>>> person2.coupon_set.all()[0].name
'가입환영 쿠폰'
더 많은 쿠폰을 뿌려보겠습니다.
>>> coupon1 = Coupon(name='배송비 할인 쿠폰', discount_price=3000)
>>> coupon2 = Coupon(name='신학기 맞이 쿠폰', discount_percent=10)
>>> coupon1.save()
>>> coupon2.save()
>>> person1.coupon_set.add(coupon1, coupon2)
'프레임워크+라이브러리 > Django' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Django] DateTimeField column으로 이것저것 해보기 / __range(), __lt, __gt, __month 등등 (3) | 2021.03.31 |
|---|---|
| [MySQL, Django]ManyToManyField를 쓰는 이유 (2) | 2021.03.30 |
| [MySQL, Django]csv 파일 DB에 밀어넣기 (bulk_create) (0) | 2021.03.29 |






댓글 영역